About Lyme Disease
GLA Funded Research
Apply for Funding
Lyme disease symptoms are wide-ranging, with more than a hundred different symptoms recorded. Symptoms can also change over time, as the bacteria spreads throughout the body. To make things more confusing, Lyme disease symptoms will also vary from patient-to-patient.
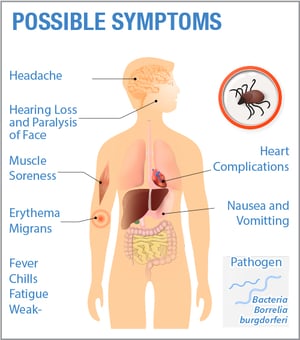 Lyme disease (Lyme borreliosis) can mimic hundreds of other conditions since its symptoms mirror many medical problems such as multiple sclerosis, arthritis, chronic fatigue syndrome or lupus, and is sometimes known as “The Great Imitator” because of this. Click here for a more complete list of possible symptoms.
Lyme disease (Lyme borreliosis) can mimic hundreds of other conditions since its symptoms mirror many medical problems such as multiple sclerosis, arthritis, chronic fatigue syndrome or lupus, and is sometimes known as “The Great Imitator” because of this. Click here for a more complete list of possible symptoms.
Symptoms can play a key role in diagnosing Lyme disease. Due to the lack of an accurate diagnostic test, many patients are diagnosed based on a combination of symptoms and diagnostic testing. This makes it extremely important for patients to keep track of all the symptoms they experience, to share with their healthcare provider.
Lyme disease symptoms can vary based on stage of the disease (early, late, post-treatment, or chronic) and if other tick-borne infections are present and can change over time.
Acute Lyme disease (aka: early localized LD) occurs days to weeks after the initial tick bite and initial infection, in which the bacteria have not yet spread from the site of infection in the skin.
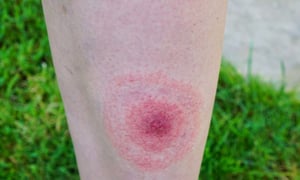 The most common symptoms in acute (aka: early localized) Lyme disease are the ones people are most familiar with, because they are symptoms often shared with other illnesses; however, it’s important to recognize that they could indicate Lyme, and you should see a Lyme-treating physician right away.
The most common symptoms in acute (aka: early localized) Lyme disease are the ones people are most familiar with, because they are symptoms often shared with other illnesses; however, it’s important to recognize that they could indicate Lyme, and you should see a Lyme-treating physician right away.
Early disseminated Lyme disease occurs days to months after infection, in which the bacteria have begun to spread. There is a wide range of possible symptoms at this stage, including:
Late stage Lyme disease, which can include post-treatment, chronic, and neurological, and chronic Lyme disease, occurs months to years after infection, in which the bacteria have spread throughout the body.
The symptoms of late disseminated disease are similar to those of early disseminated disease, but may be more extensive, more severe, and longer lasting. Late symptoms may also include:
Join our community of advocates by subscribing to our newsletter—stay informed with the latest breakthroughs in Lyme disease research and news. Ready to take the next step? Your donation to Global Lyme Alliance fuels the fight for a cure.
Subscribe Now to stay involved, or Donate Today to help us overcome Lyme disease.
In the United States, you can become infected with Lyme disease from blacklegged ticks, also known as deer ticks. First step to prevent Lyme disease is to prevent tick bites. Prevention goes beyond wearing long-sleeved shirts and insect repellent in wooded areas. Be sure to check out GLA's Lyme prevention tips, especially if you spend time outdoors or live in an endemic area.
As soon as you have visual proof of a tick bite (if you find it, remember to save the possibly infected tick and send in for testing). Additionally, if you suspect Lyme disease based on the symptoms listed above, consult a Lyme treating physician. The sooner treatment is started after a tick bite, the more effective it is.
No. The absence of symptoms does not mean the disease is gone. It’s important to consult with your doctor even if symptoms disappear.
It’s important to remember that up to 20% of those diagnosed and treated early will continue to have symptoms. This means that even if you have undergone treatment, you could still have Lyme disease. Keep track of all symptoms and share with your healthcare provider.
It remains unclear why some patients, despite antibiotic treatment, continue to experience persistent symptoms of Lyme disease and other tick borne diseases. Possible explanations include persistence of antibiotic-tolerant bacteria, autoimmunity triggered by prior infection with the Lyme bacteria, or perhaps co-infection with other tick-borne pathogens. These mechanisms of chronic disease are not mutually exclusive.
If you suspect Lyme disease, even though you don’t recall a tick bite from outdoor activity or a rash, it’s important to consult with a Lyme physician right away. Untreated, Lyme disease can spread to other parts of your body for several months to years after infection, causing arthritis and nervous system problems.
Lyme disease is relentless, but so are we. Your donation powers the research that leads to breakthroughs and patient service programs that prevents suffering. Stand with us in the fight—your contribution can create lasting change and future relief for so many.
Donate Today and Be a Part of the Solution.
2023 © Copyright Global Lyme Alliance. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer: The above material is provided for information purposes only. The material (a) is not nor should be considered, or used as a substitute for, medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment, nor (b) does it necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of Global Lyme Alliance, Inc. or any of its directors, officers, advisors or volunteers. Advice on the testing, treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history. Global Lyme Alliance, Inc. makes no warranties of any kind regarding this Website, including as to the accuracy, completeness, currency or reliability of any information contained herein, and all such warranties are expressly disclaimed.